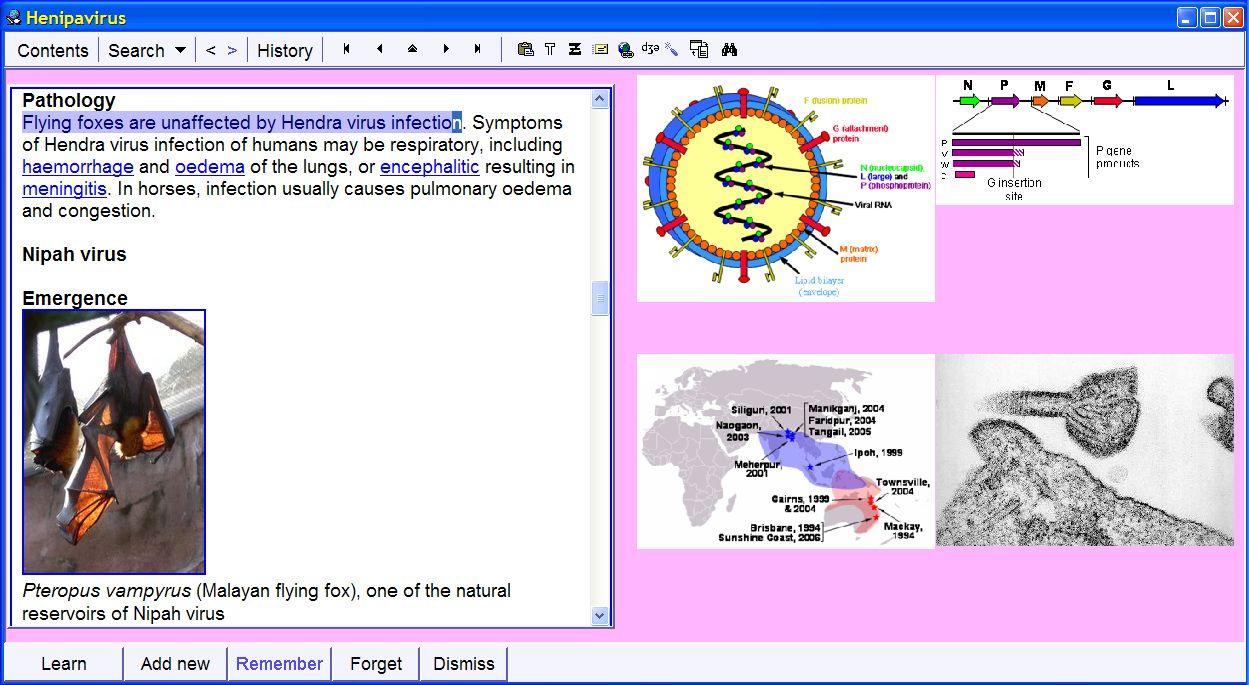
| What's new in
SuperMemo 2006 |
Summary
The most important improvements to SuperMemo 2006 as compared with SuperMemo
2004:
- The priority queue makes it possible to increase
the volume of
incremental reading and still improve retention on mission critical material
- Incremental reading now uses automatic
priority setting to make sure you spend minimum time on pondering
priorities
- Fast repetition scheduling
substantially speeds up SuperMemo and allows of new functionality that was previously not
possible (e.g. auto-sort, auto-postpone, etc.)
- Repetition auto-sorting ensures that you begin each learning day from your
top-priority material
- Repetition auto-postpone ensures you never need to worry about the
overload of material for review
- Incremental reading with pictures is now easy. For the first time, having
most of your articles and items illustrated with pictures may become a norm
rather than an exception:
- Import from Wikipedia takes one
keystroke instead of a series of up to 10
operations and no less than 30 seconds in SuperMemo 2004
- Import : Files and Folders allows you to import to SuperMemo the
entire folder structure of your file archives (e.g. picture albums)
- Collection chooser provides the fastest
way to open collections with a single keystroke
(usually the first letter of the collection's name)
- Stylesheets in HTML components and
templates make it easy to globally change formatting of texts (e.g.
fonts, colors, etc.)
- SuperMemo use statistics will now help
you see more statistics, further back in time, and with more detail
- Decompose and
Dismember in
incremental reading accelerate the conversion of elements that conglomerate
information into easy-to-learn well-formulated pieces of knowledge
- Hiding SuperMemo in the system tray (Ctrl+Shift+G) makes it
possible to keep
the alarm timer going while working unobtrusively with other applications.
Restarting SuperMemo from the tray is instantaneous
- Faster element browser opens thousands of elements instantly (previously,
huge collections might take minutes on PCs with less memory)
- Inserting registry
objects to elements is now simpler. For example, with a click on the
browser toolbar, you can choose a picture to illustrate all elements stored
in the browser. Elements that already include pictures can have them tiled
conveniently
- Quick splitting of large
articles in incremental reading with split-marks
- Postpone is now less detrimental as the degree of
delay depends on element's priority
- Unicode titles can now also be displayed in the contents window
- Tiling components makes life easier in
elements with multiple components (e.g. pictures)
- Improved multiple choice tests
now allow of all component types and all image formats
- Some of the deprecated options have
been removed to reduce option clutter and make the program faster and/or
more compact
- See also: Minor
improvements, bugs and annoyances
Priority Queue
Priority queue is the most important new feature of SuperMemo 2006. With the
new priority system in SuperMemo 2006, as well as with huge hard drives, large memories and fast
computers, only your available time is now a limit on how much
material you can handle with SuperMemo. Even your memory is no longer a factor
due to the fact that you can store low-priority low-retention material without
affecting the mainstream learning process. You may still want to pause before adding
excess material to your collection, but your learning overheads will only depend
on how accurately you define the priority of such imports.
The priority queue makes
it easy to sort the learning material by priority. Each element in SuperMemo
2006 carries a number called a priority. Priorities are relative. This
means that newly inserted high-priority elements displace previously inserted
elements of lower priority. Reducing the priority of one element, increases the
priority of other elements. The entire learning process proceeds along the
priority criteria. This means that you will never neglect your
top-priority material. Even if your collection holds far more material than you
can ever hope to process and learn. You will now always begin your reading with
top priority articles or extracts. You will make sure that the retention of your
top-priority items is strictly determined by the forgetting index only. On the
other hand, you can accept an overflow of lower priority items marked by a higher
tolerance for forgetting. Those items will still make a valuable part of your
learning. Due to the spacing effect, you will be able to increase the
speed of acquiring new material even though, within lower-priority ranks, you
will lose some control of which portions of your learning are retained in memory
and which might be forgotten.
For details see: Priority Queue
Automatic priority setting in incremental reading
In incremental reading, extract priorities depend on a number of factors. Primarily, they are derived
from the priority of the parenting topic. The higher the priority of the parent,
the higher the priority of the extract. However, for very high priorities,
extract's priority is likely to be lower than that of the parent, while for low
priority articles, extract's priority may be much higher than that of the article. This
is because high priority articles are supposed to be read slowly line by line and generate many
extracts, while low priority articles are only skimmed or speed-read while fishing for extracts. Length of the extract also affects its priority, with short
extracts receiving a higher priority. This is because long extracts are usually
created for the sake of later reading, while shorter extracts are more likely to
contain meaningful information that is only a step away from generating cloze deletions. Finally, a tiny degree of randomization is added in
generating extract priorities in order to prevent clustering of extracts coming
from the same article while making repetitions sorted by priority.
Priority of cloze deletions is similar to that of the parenting extract. To
prevent the clustering of items derived from the same extract, as well as to
avoid spacing effect and interference, priorities and the first intervals of
cloze deletions are dispersed randomly around the presumed optimum value.
Fast repetition scheduling
Some of the repetition scheduling procedures in the previous versions of
SuperMemo for Windows have been inherited from SuperMemo 1.0 for DOS (1987)!
Those procedures were optimized for times where disk space was tiny and computer
memory was limited to 640 KB (i.e. a few thousand times less than an average PC
today). In SuperMemo 2006, large structures related to the repetition schedule
are kept in memory and periodically saved to the disk to ensure negligible
sensitivity to errors on power failure. This makes it possible to increase the
speed of some rescheduling procedures by up to 200 times (esp. Postpone, Mercy,
Reschedule, Sort repetitions, and repetition schedule verification
at Repair collection, etc.). Rescheduling operations now proceed at
10,000 elements per second on an average PC. Most importantly, new functionality became
possible only with fast repetition rescheduling. In particular, auto-sort and
auto-postpone options that now, by default, begin your each learning day would not be
possible in SuperMemo 2004.
Import from Wikipedia
Edit : Add to category : Wikipedia (Ctrl+Shift+W) makes it easy to import
articles from Wikipedia in incremental reading. All Wikipedia articles opened in
Internet Explorer will be imported upon confirmation. If no articles can be
found,
SuperMemo will open the article whose title matches the
text currently selected in SuperMemo. If no text is selected, SuperMemo will ask for the title of
article to import. If no such article exists in Wikipedia, SuperMemo will
initiate a search for the term of interest in other Wikipedia articles. Upon
import, each article is filtered to remove junk tags irrelevant in learning
(e.g. navigation options, search boxes, alerts, funding requests,
redirections, section edits, tables of contents, etc.). All articles become
tagged with Wikipedia references, the title, the date, and the link to the
original article. Those references propagate into all extracts and clozes in
incremental reading. Only
table filtering and image imports are left at your discretion.
Import : Files and Folders
Import : Files and Folders allows you to import to SuperMemo the
entire folder structure of your file archives (e.g. picture albums,
collections of archive articles, miscellaneous to-do files, etc.). You can
clean up your file archives with a single keystroke and process them
incrementally with tiny allocations of time each day. Instead of keeping
your family picture archive in mothballs, you can now come back to selected
memories in a systematic manner. You will be surprised how much you can
learn from old pictures and how addictive the whole process can be. You can
finally clean up the archive of articles you have downloaded from the web for
later reading. Incremental reading will provide a systematic and rational way of
matching your reading ambitions to the available time. You can apply
incremental processing to any imaginable to-do file archive by importing the
archive to SuperMemo.
Collection chooser
Collection chooser helps you quickly access your most frequently used
collections. Instead of navigating through folders with File : Open
collection, or searching for the right collection number of the pick-list on
the File menu, you can simply press Ctrl+O and the letter that
designates your collection (e.g. K for Knowledge as in the picture
below). You decide which collections will show up in the chooser by adding them
with the button Choose another. You can still use the pick-list
for recently used collections and File : Open collection for less
frequently used
collections that are absent from the chooser or pick-list. Collection chooser is
also used in various contexts where you need to pick a collection. For example,
if you want to transfer an element to another collection, SuperMemo will open
the collection chooser to help you pick the destination collection.

Improved image downloads
Temporary Internet Explorer cache is used to instantly
retrieve files without the need to download. For a default cache size, this
provides instant access to 95% of image files. This statistic may not apply to
articles with multiple images immediately after opening the article in
SuperMemo (i.e. at a time when HTML component is still downloading the images
via http). Multiple images can be tiled to illustrate a single article.

Improved web import
The following import modes are available for web pages opened in Internet Explorer:
- Links only creates separate elements each holding a single link to
a single article
- Page of links imports all links to a single element
- Local pages imports entire web pages to separate elements
- new: Local pages with local images works like Local
pages but all images found on a page are tiled
as separate image components in the right portion of the element window
- new: Local images only imports only images from individual web pages.
Each page, if it contains images, produces a separate element with all
images imported and tiled
- new: Page of images imports selected images from selected pages
to the current element or into a new element. The images are tiled at import
- Live links imports links to articles like Links only except
that the links open live pages when the element is entered in SuperMemo
Example: imagine you are studying the landscapes of the Lost Coast and you
open a few articles on the subject in Internet Explorer. Here are some of your
choices:
- If you want landscapes stored in image components, but you still want to
import the accompanying texts, use Local pages with local images
- If you are interested in landscapes only, use Local images only. In
this case, web pages that contain images will produce separate elements with
images tiled (one element per page). Images opened in the
browser will import into separate elements with a single full-screen image component
- If you are interested in using landscapes to illustrate existing articles
in SuperMemo, use Page of images
- If you want to import all images from all opened web pages into a new
article, use Page of images. Answer No to Import all pictures to the current element?.
You can later delete some images and move the remaining ones into
separate elements with Dismember
Disclaimer: not all pages and not all images can be processed using SuperMemo
web import. Some pages and images generated programmatically may need to be
imported manually via copy&paste. This problem affects 1-2% of typical pages and/or images.
Image zooming, trimming, compressing and cutting
Several new operations on images help you save space and better illustrate
your articles in incremental reading:
- Zooming and trimming can be used to display only a part of a larger picture
inside an image component. For example, you can import a large high-resolution map of
Africa. The map may be larger than your screen. You can then
formulate individual geography items on individual countries of Africa and zoom in on that part of the picture that is of
relevance for each item. To gradually zoom out, Ctrl+click the picture while in the zoom
mode
- Trimming can be used to cut borders of images that go beyond what you need
to represent. After choosing Trim, you can cut the edge of a picture with
a single mouse swipe (press down the left mouse button and move the unwanted portion of the picture out of the picture area). The trim affects the image file only after you apply Image
: Cut on the component menu. Before you use Image : Cut, the
trimming is reversible
- Images can be scaled, compressed or reduced in quality to save disk space
and reduce load times. Instead of holding a 2 MB family picture, you can easily store
a 300
KB file without a noticeable loss of quality (at monitor resolutions of up
at 1600x1200). In scaling
pictures, you can chose the target size of the file, or scale
gradually with a trackbar and preview
Tiling components
This option makes it possible to choose components from the component list
for tiling. By default, all components in editing and dragging
modes are checked for tiling. The tiling covers the maximum
rectangle currently covered by the most extremely placed components on the list.
To change the tiling area, move the extreme components to new locations. Tiling
is used automatically by default in several contexts, e.g. pasting images to an
element.
Exemplary topic with images auto-tiled at image download:
Picture templates
It is now easier to use picture templates. If you take any template, add a picture to it, and then name the new template by adding 'Picture'
or 'P' to its name, you can have SuperMemo automatically use that
template in elements where pictures are used. For example, if your category has a
default item template called 'Geography', you can create a picture
template, name it Geography Picture or GeographyP (without a
space). You will then be prompted to use this template in cases such as: moving an
element with a picture to any category where Geography is the default
template, pasting picture to elements with the Geography template
applied, generating cloze deletions in categories where Geography is the
default item template, etc.
Inserting registry objects
was made easier
SuperMemo 2006 simplifies adding components by making it easy to insert selected registry
members into elements. To insert a picture to many
elements you previously had to use templates or tediously repeat Links : <Registry> : Accept
in many elements. Insert in registries now makes it possible to open the image in the
registry, leave the registry in the background, move between elements, and add pictures
to elements with a single
click on the Insert button in the registry. A new option, Template : Insert picture in the
browser (on the subset operations menu) makes it easy to
illustrate the entire subset of elements with a selected picture. Finally, Insert in registries
simplifies organizing components in the element by shifting or tiling components
to make room for new inserts.
Operation Decompose in incremental reading
The operation Decompose makes it possible to generate multiple topics or multiple items from
enumerative elements.
For example, the following cloze violates the minimum information
principle:
Q: The levels of serotonin, acetylcholine, noradrenalin, and
somatostatin all [...] in
Alzheimer's
A: decrease
This cloze can easily be edited to the following form:
Q: The level of {serotonin/acetylcholine/noradrenalin/somatostatin} [...] in
Alzheimer's
A: decreases
Upon applying Decompose, it will be be converted to 4 cloze deletions such as:
Q: The level of serotonin [...] in Alzheimer's
A: decreases
Q: The level of acetylcholine [...] in Alzheimer's
A: decreases, etc.
The option Decompose can be found on the component menu
as Reading : Decompose.
Operation Dismember
in incremental reading
The operation Dismember makes it possible to generate multiple elements from
multi-component elements.
For example, if you receive mail with multiple picture attachments and import
this mail to SuperMemo, you can use Dismember to produce separate
elements for holding each picture. Selected components (e.g. mail body) can be
chosen to propagate to child elements for retaining the context. This way,
individual attachments or pictures can enter the review process as separate
elements.
The option Dismember can be found on the element menu as Edit : Dismember.
Stylesheet registry
Stylesheet registry can hold a set of stylesheets that can be used to format
HTML texts in individual components or in templates used throughout the
collection. Stylesheets can also be used to customize the appearance of
extracts, cloze deletions, headers and references in incremental reading. A
mini-editor for styles was included for those who do not know stylesheet
specifications (CSS).
SuperMemo use statistics
SuperMemo will now display use statistics without cutting off old data. You
will be able to view some of the data back as far as from the moment you started
using SuperMemo 2002 (e.g. Use : Element count : Items). The graph
clutter can be solved by sweeping off portions of the graph with the mouse
(press down the left mouse button and move the unwanted portion off the graph
out of the graph area).
SuperMemo will also use timeline statistics to recover some of the past data
from the moment you started using SuperMemo 2004 (e.g. Use : Work done : Use
time).
Finally, SuperMemo 2006 introduces new use statistics that will be collected
as of the moment of the upgrade to SuperMemo 2006 (e.g. Use : Efficiency :
Retention).
Quick splitting of large articles
To speed up splitting large articles, you can now insert split marks and
execute Reading : Split : Split Article (on the component
menu). The article will be cut into smaller portions
separated by split marks. To insert a split mark you can:
- choose Insert split mark on the component menu
- type sp and press Ctrl+Shift+1
- paste a split mark from other places in the document
Degree of
Postpone depends on the element's priority
In earlier versions of SuperMemo, you could define a degree of delay when
postponing a subset of elements. Now the delay is modified depending on the
priority of an element. For example, if the delay factor is 1.1 (i.e. all
intervals are to be increased by 10%) then the modified delay is spread in twice
the range of the delay factor: from 1.0 to 1.2 (1.0 for highest priority
elements and 1.2 for lowest priority elements). After the modified delay is
computed, minimum and maximum delay interval limits are imposed. Finally, the
increment in the interval is dispersed randomly around the proposed value. The
dispersion follows a normal distribution with cut off points between 50% and
150% of the proposed value. For example, if the delay factor of 1.1 produced an
interval increment of 20 days, the actual increment will fall in between 10 and
30 days. As delay increases faster than the drop in priority, average delays should be
more significant except where limited by maximum delay interval.
Improved multiple choice tests
Multiple choice tests can now use all component types (e.g. HTML, RTF, etc.).
All image
formats available in SuperMemo can be used in tests.

Reduced option clutter
SuperMemo 2006 sheds vast amounts of code used to implement options which became
obsolete or deprecated. This helped reduce program's size
and complexity as well as to increase its speed in a number of operations.
Please read the list of options removed before you decide to upgrade:
- Import from SuperMemo 1.0 to SuperMemo 7.0 is no longer supported
(use earlier versions to upgrade; trial versions are enough). Multimedia file
structures from SuperMemo 7.0 are no longer supported (use Internalize in
registry with the help of earlier versions of SuperMemo).
- Separate options for
sorting the pending queue have been removed. The same function can be
accomplished by saving a sorted browser into the pending queue
- Reference tag #Image is no longer supported. Old tags will still
proliferate in extracts, but new tags cannot be created (unless manually in
HTML). This option has been removed due to the dynamic nature of the web
that leaves most of old #Image tags useless after some time. Using
this tag often traps users with material that is no longer valid. Importing
images locally is now the recommended solution for learning with pictures.
New image importing, trimming and sizing options should make it possible to
even import small illustrative pictures of lower importance, esp. in the
light of the ever increasing availability of cheap hard disk space
- Add URL dialog box has been removed along with options such as Edit
: Add to category : Web page, etc. Those functions can now better be
accomplished with Edit : Import web pages (although this requires
Internet Explorer 6 or later)
- Reset parameters : Repetition history has been removed as well as
the Full repetition history option. As of SuperMemo 2006, full
repetition history is obligatory as the basis of important functionality
(now and in the future)
- Auto-sort and auto-scroll have been removed from the
contents window
- It is no longer possible to replace SuperMemo algorithm with a customized
algorithm in a DLL. In 10 years since introducing this option, there were no
reports of DLLs developed outside SuperMemo World
- SuperMemo 2006 is no longer programmable. Writing DLLs for SuperMemo did
not take off and removing programmable SuperMemo procedures substantially
reduced the size of the code. Some learning options will also execute faster
Minor improvements, bugs and annoyances
The complete list of changes to SuperMemo 2006 is 989 positions long. Here
are some minor improvements that could make a major difference to some users:
Improvements
- Customizable web search for a phrase that is currently selected in
SuperMemo (through dictionaries,
encyclopedias, databases, blogs, or sites and services of your choice, etc.)
- Find button on the element toolbar helps searching through longer
texts. In HTML texts, all occurrences of the found string are highlighted. F3
can be used to jump between highlighted matches
- Ctrl+Shift+E to send the current element via e-mail
- Shift+click for editing pictures
- Q&A export may now include HTML tags
- Postpone makes it possible to postpone all elements except a set
number even if they do not meet postpone criteria
- Copy, Paste and Move for elements in the knowledge tree
(Contents)
make it possible to use keyboard for rearranging the tree (instead of the
mouse and drag&drop operations)
- Workload graph can be used to visually inspect the number of
elements scheduled for review in future months and years (the display can be
dragged with the mouse to scroll as far ahead as the most remotely scheduled
element)
- New shortcut, Shift+Alt+X
(same as Alt+X for Remember extract with Shift pressed),
makes it easy to set the priority of a new topic at the moment of extracting
it in incremental reading
- Repetition history stores the precise time of a repetition (for circadian
research and future optimization of learning time in SuperMemo)
- Q&A import supports ANSI, UTF-8, little endian UTF-16, and big endian UTF-17
- Alt+R for a fast rename of the registry member associated with the
current component
- Image components show hints with image registry member name, file name and
path, file size, date, etc.
- Improved memory manager (courtesy of Delphi 2006) speeds up operations
requiring vast allocations of memory
- Possibility to shift a repetition to "later today" (Ctrl+Shift+J)
- Picture forwards may be compressed before sending
- Picture forwards may optionally include only the zoomed portion of the
picture
- Element and picture forwards via e-mail leave forward data in the comments
field (e.g. to prevent forwarding the same information twice)
- Image : Use as : Windows
desktop
- Image : Use as : About box
- Image : Use as : SuperMemo background
- Delete components makes it possible to uncheck components that
should not be deleted
- Sorting elements in the order of occurrence in the knowledge tree in the
browser
- Child : Descendants in the browser to find extracts
and clozes produced by a set of articles
- Item and topic overload statistics (Analysis : Use : Overload)
- Reducing size of HTML files and automatically converting some of HTML to
plain text
- When importing pictures, repeated imports of the same picture from the same URL will keep only one image in the registry
- Item repetitions can be advanced in a way similar to topic advancement.
The difference is that absolute intervals will be shortened as
opposed to topics where the interval is shortened relative to the day of
execution
- Search and Replace makes it possible to do global replace without
using the text registry. In certain cases, depending on the size of the
registry and number of replace hits, using the text registry may still be a
better choice due to speed
- Skipping text statistics in subset statistics can speed up the operation
20-50 times
- Tools : Plan allows of keeping Monthly and
Annual statistics of daily activities exportable to Excel. Accessory
statistics can also be compiled (e.g. jogging time, calories consumed,
visits to the cinema, injuries, etc.)
- WMA support
- Resizable text input dialog box for longer texts
- Ctrl+Shift+click can be used to reset reference hyperlinks
- Faster display of data in daily and monthly workload windows
- Browser toolbar can be used to quickly generate a child browser with all
selected or all unselected elements of the current browser
- Ctrl+Shift+B in registries displays a browser with elements that
use only the selected registry members (previously all members of the
current registry subset were used)
- Split in Plan uses the time that elapsed from the beginning
of the slot as the split default (previously, the slots would be cut in half
by default)
- Author, Date and Source references in incremental reading can be chained
in the same way as titles (e.g. New Scientist : Neuron)
- Collection chooser does not allow of opening incomplete collections to
prevent confusion in cases where the user moves the kno file without
the accompanying folders
Bugs and Annoyances
- Mshtml errors in incremental reading are now nearly extinct once Internet Explorer 7.0 is installed
- Pictures, subscripts and superscripts are marked in registry names to
prevent confusion between text-less HTML and mathematical texts that differ
only in subscript/superscript formatting (Full HTML attribute must be
on)
- Minimize button was absent from the toolbar dock
- Pet annoyance of non-English keyboard users, Trim Shortcuts, is no longer needed
- All image conversions are now possible (BMP, JPG, GIF, PNG). Previously,
image compression and format choice were not reversible
- Changing midnight shift would not reload the outstanding queue
- Binary components would not transfer between collections
- Edit : Save file with binary components would not remember the last
used path
- Postpone no longer annoys with Reload browser? inquiry. As
the browser is now much faster, it reloads instantly without asking
- Progress box would hide behind the Postpone dialog when switching
between applications
- Alarms are now raised by displaying a non-modal dialog box
- Zero-sized remote images could hang the download procedure
- Toolbars would cover Plan when switching to other applications
- Some animated GIFs could hang SuperMemo
- Not all PNG images could be displayed
- Registry Unicode sorting changed from UTF-8 to UTF-16 with fewer sorting
surprises
- Image download dialog box could not be resized and would not size label
font for better readability
- Q&A import would impose the import template on newly created items
(instead of just applying it)
- Pictures with non-ASCII codes in their names would not import
- Search for Clinton with match words would not find Clinton's
- Annoying progress bar no longer shows on filtering or importing longer
texts (these operations are now fast enough to be dealt with just an
hourglass)
- Interval distributions would display range check errors for Topics + Items
> 65536
- Collections would not open in read-only mode on a DVD-R
- Feedback questionnaire is now saved between sessions and may be sent
later
- In video extracts, playback start and end positions would be occluded by
video templates
- Sounds would play via Auto-Play at question time even if Play At was set to answer time only
- De-HTML-ize would not cut preceding tags at the beginning of texts
- Case conversions would ignore HTML tags
- FAQ dialog would require an empty FAQ html file exist before storing FAQs
- FAQ dialog could not be sized
- Removing date picker prevents tinkering with the date in SuperMemo
(although it is still possible in Windows)
- Mail attachments would use numeric file name instead of the actual
registry name
- Solving problems with import of mail from non-English Outlook
- Mail import goes to a single, dated folder
- Element titles could hold long texts that would produce false search hits
- References are no longer cached. If you edit their texts, the edits will
show up in new extracts
- You can now paste sounds
- HTML templates in the template registry could produce "Error retrieving background
color"
- Align button in the browser would not restore the browser window if it was
maximized
- Many dialogs were enlarged to allow for a larger font
- Intervals beyond 40 years from setting up a collection would not be
accepted
- Very long entries in Plan would be cut without warning
- Alt+Backspace in Plan would bring up the element window
- Exports from Plan would get confused by HTML markup if it was
included in the schedule

